
IT Security
August 2nd 2024
Ransomware Attack starts with cybercriminals hacking a system and encrypting all data. Then, if the victim agrees to pay a ransom through cryptocurrency, cybercriminals offer a decryption key.
In addition to entering a system and depositing encrypted malware, some ransomware operators will utilize multi-extortion techniques to boost payment, liking threating and shaming victim on social media and add on attacks like leaking the sensitive stolen data, copying and exfiltrating the encrypted data to client or on the dark web.
What is Ransomware Attack?
Ransomware is malware developed to neglect an organization or user access to different data and files on their computer. Also, by encrypting these files they demands a ransom payment for the cyberattacks, decryption key. As paying the ransom is the cheapest and easiest ways to regain access to all the data.
Also, some variants have added additional functionality, like data theft to offer further incentive for ransomware victims to pay the ransom.
Types of Ransomware Attacks
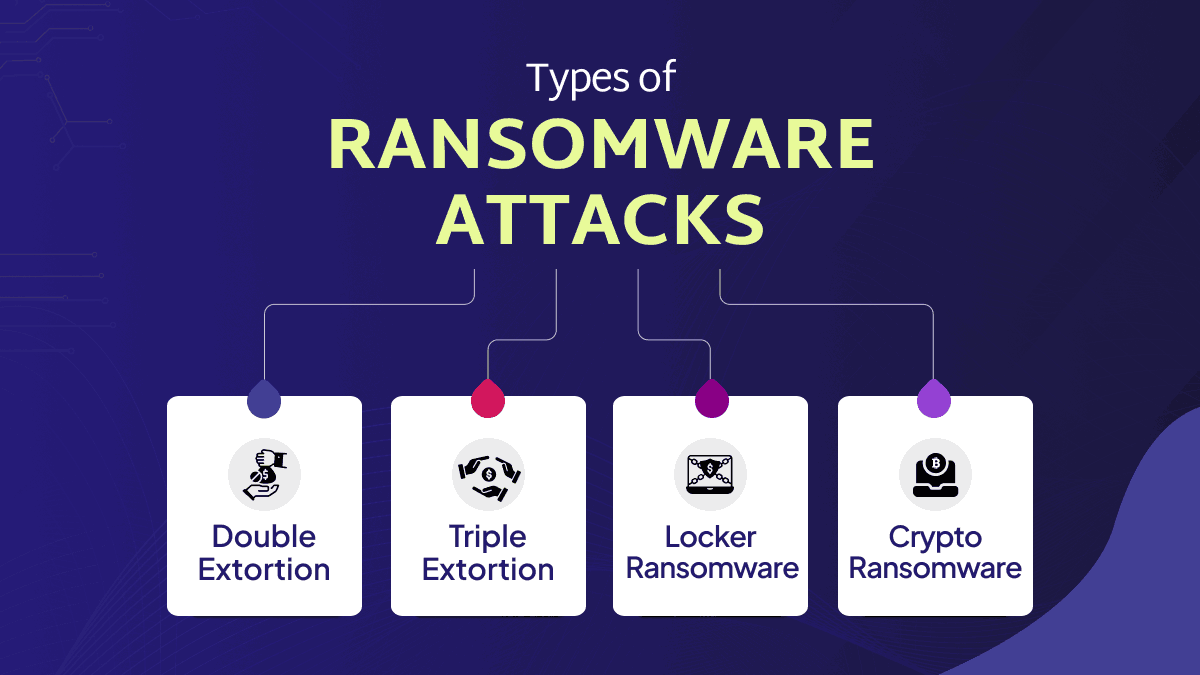

1. Double Extortion
Double-extortion ransomware like Maze combines and merges data encryption with data theft. This technique was designed and developed in response to organizations refusing to pay to restore and ransoms from backups instead. Also, by robbing and stealing an organization’s data, the cybercriminal cloud threatens to lead it if the victim does not pay up.
2. Triple Extortion
The double extortion ransomware is enhanced into triple extortion ransomware by adding another form of extortion. In addition, it includes asking ransoms from victims’ clients or business associates or launching DDoS attacks against the company itself.
3. Locker Ransomware
The Locker ransom virus does not encrypt files on the victim’s computer. Instead, it locks the system making it impossible for the victim to use their own machine until they have paid a ransom.
4. Crypto Ransomware
Crypto ransomware is another term for ransomware that highlights the fact that it is often paid in cryptocurrencies. This is due to the fact that they can be hard to trace since they are outside the realm of mainstream finance. This is because they are more difficult to track since the traditional financial system needs to manage them.
How Does Ransomware Work?
Ransomware must easily gain access to a target system and demand huge ransom from the victim to restore their information and files. Also, the implementation details differ from one to another.
Now you may question about How does ransomware attack work? Regardless of the definition of ransomware, once it enters your computer, it secretly infects it. The software then proceeds to attack access and files and change login information without the user knowing. Consequently, the individual in charge of the infection is essentially holding the computer infrastructure hostage.
Step 1. Infection and Distribution Vectors
Ransomware, like any malware, can easily gain access to a business’s system in several different ways. Moreover, ransomware operators tend to prefer a few specific infection vectors.
A further example of this is phishing emails. A malicious email could have an attachment with downloader functionality or a link to a website that hosts a malicious download. Therefore, if the email recipient falls for the phish, the ransomware is quickly executed and downloaded on their computer.
Another most popular ransomware infection vector takes advantage of services like Protocol for Remote Desktop (RDP). An attacker can remotely access a machine within the company network by using RDP to authenticate and guess the login credentials of an employee.
Step 2. Data Encryption
Ransomware virus can begin encrypting files on a machine once it has obtained access to it. Since operating systems come with encryption built in, all that needs to be done is access the files, use an attacker-controlled key to encrypt them, and then replace the original files with the encrypted ones.
Well, most ransomware variants are more cautious in their file selections to encrypt to make sure system stability. In addition, some variants may also take steps to delete backup and shadow copies of files to make a recovery without the decryption key more difficult.
Step 3. Ransom Demand
Once the file encryption is completed, the ransomware is developed and prepared to demand a ransom. Different ransomware variants also implement this in numerous ways. Still, it is not uncommon to have a display background that can be changed to a ransom note or text files placed in each encrypted directory containing the ransom note.
These notes usually want cryptocurrencies in order to grant access to the victim’s file. The ransomware operator will provide the copy of the encryption key or a copy of the private key that was utilize to give protection.
Ransomware Removal: How to Deal with an Active Ransomware Infection
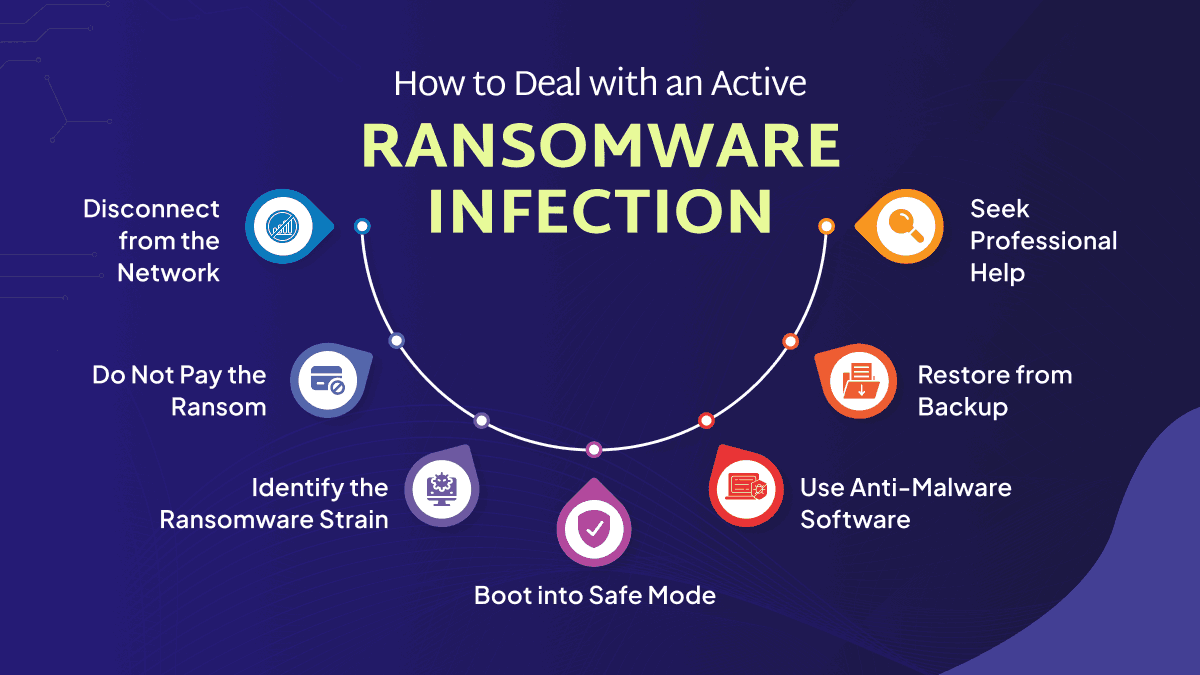

1. Disconnect from the Network
When you realize your system has been infected with ransomware, the first step is to quickly disconnect the impacted and hacked device from the internet and any local networks. This action helps to contain the infection and prevent the ransomware from hacking other devices on the same network.
2. Do Not Pay the Ransom
It may be tempting to pay the ransom to quickly regain access to your files, but doing so is not recommended. Paying the ransom does not guarantee that the attackers will restore your access. Furthermore, it encourages and funds criminal activities. Instead, focus on alternative solutions such as restoring from backups or seeking professional assistance to recover your data.
3. Identify the Ransomware Strain
Identifying the specific strain of ransomware that has infected your system can help in finding a solution. Use online resources like ID Ransomware, where you can upload the ransom note or an encrypted file to determine the type of ransomware.
4. Boot into Safe Mode
Restart your computer and reboot into Safe Mode to prevent the ransomware from actively running. For Windows, restart the computer and press F8 (or the appropriate key) during boot-up to enter Safe Mode.
5. Use Anti-Malware Software
Run a comprehensive scan using reputable anti-malware software to detect and remove the ransomware. Programs like Malwarebytes, Bitdefender, and Kaspersky are highly recommended for their effectiveness.
6. Restore from Backup
If you have recent backups of your files, you can restore your system to a state before the ransomware infection. Ensure that the backups were not connected to the system during the infection to avoid contamination.
7. Seek Professional Help
If you are not able to remove or delete the ransomware or recover your files on your own, it is advisable to seek professional help. Cybersecurity professionals can provide specialized tools and expertise to handle the infection. Contact a local IT support service or a cybersecurity firm for assistance.
Summing Up
It is obvious that preventing a ransomware attack in the first place is the best defense against one. Apart from that, if you ever become the target of an attack, you may minimize downtime and data loss by ensuring your important data is backed up and inaccessible due to a ransomware outbreak.