Cloud Industry
June 17th 2024
Organizations are rapidly seeking scalable, flexible, and effective ways to manage their IT infrastructure. Therefore, one of the most innovative ways to manage IT infrastructure is through Hybrid cloud solutions. This blog delves into what hybrid clouds are and their process. Also, we will understand its benefits for businesses.
What is Hybrid Cloud?
A hybrid cloud is a storage and computing infrastructure composed of a mixture of private cloud services, a public cloud, and/ or on-premises infrastructure. The various resources are arranged to work together as seamlessly as possible.
Therefore, with a hybrid cloud, businesses can obtain the “best of both worlds.” They can utilize cloud services where they operate best while keeping certain operations within their on-premises network infrastructure or inside a private cloud.
This helps to ensure greater flexibility. There are several hybrid cloud types, and regardless of the solution you select, it is vital to ensure the security of your hybrid cloud environment.
How does Hybrid Cloud work?
With the help of the hybrid cloud, businesses deploy workloads in Private IT environments or public clouds, incorporating IaaS, SaaS, and PaaS. They can often move workloads and data between them as computing needs and costs change. This setup offers organizations greater flexibility and more options for data deployment.
A hybrid cloud workload incorporates an application’s hosting, network, and web service features. Also, they can simultaneously include the components that include:
Local
In this traditional local center, one or more applications are deployed. These local workflows are considered critical where regulatory or business pressure requires the organizations to exert direct control over the application, regional infrastructure, applications, and data.
Cloud
One or more applications and data stores are deployed to selected regions in this public cloud provider. These deployments reflect less critical or less used workloads, data, and short-term or experimental implementations. The business manages and interacts with the public cloud through the cloud provider’s web portal and APIs. It’s becoming common for an enterprise to utilize multiple public clouds to benefit from each cloud’s unique resource or service offerings.
Pass and SaaS
More than one application and data store are hosted by SaaS and Pass providers; the workloads are primarily business requirements selected not to deploy and run in-house. SaaS examples include finance, business intelligence, accounting, and software development toolkits.
Critical Features of Hybrid Cloud
1. Portability
Workload portability is the ability to move and adapt applications and data between cloud and on-premises systems provider to other. It vital when considering a service or application and is frequently noticed through the adoption of open-source standards and APIs.
2. Data Integration
Data integration is the process of gathering data through different sources that helps to gain more visibility and ensure a seamless shift to cloud computing. Historically, most organizations stored data in stand-alone silos or separate data stores. Therefore, real-time telemetry and insights are vital to the success of digital transformation strategies and to compete in an increasingly digital world.
3. Security of the Hybrid Cloud
As the hybrid cloud environment gathers between two environments, security for the hybrid cloud must protect data and applications both on-premises and in the public cloud and protect data and workloads as they shift between public clouds and private clouds or data centers.
Types of Environments Found in Hybrid Clouds
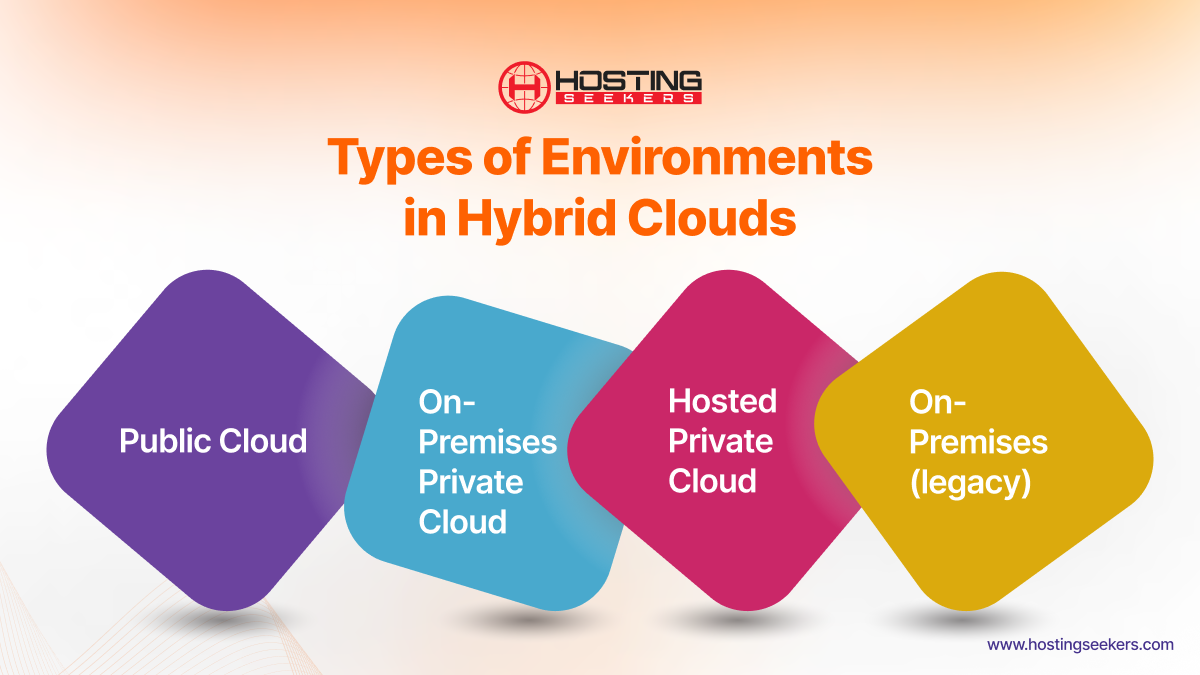

1. Public Cloud
A public cloud is an IT setup like OpenStack, where a third party manages the infrastructure and computing. Resources are shared between more than one business over a public internet connection.
2. On-Premises Private Cloud
An on-premises private cloud infrastructure is used exclusively by a single organization, which can have multiple business units utilizing the resources. The hardware and equipment that form this cloud are maintained on the organization’s premises.
3. Hosted Private Cloud
A hosted private cloud is off-premises, meaning it is in a different physical location from the organization’s premises. It is also managed and hosted by a third-party provider.
4. On-premises (legacy)
With an on-premises setup, the infrastructure is kept on-premises and supported by an internal data center. It can also be tied to cloud hosting services.
Benefits of Hybrid Cloud
1. Scalability
One of the primary and main benefit of a hybrid cloud is scalability, which aids in maintaining, establishing, and expanding infrastructure. Leveraging public cloud options, adding computational power, and running complex, resource-intensive applications becomes easier. Its setup allows for seamless scaling without purchasing additional servers. Instead, you can utilize the resources provided by the cloud service, making it an efficient and cost-effective solution for managing increased workloads and demanding applications.
2. Security
Hybrid Cloud infrastructure can benefit your organization by offering the security of a private cloud and the power and options that mostly come with a public cloud. In addition, data stored within a private cloud environment will need to be sent to the public cloud, where it is processed and utilized by applications, analytics systems, and other processes.
Therefore, to ensure encryption methods, you must ensure your data stays safe throughout the process. With a hybrid cloud, the IT team has various options for transferring and storing the data more safely.
3. Cost
A hybrid cloud helps lower long-term prices, freeing up some headroom in a business’s budget. Also, it is easier and more cost-effective to scale as it helps to save money during the growth process. Moreover, because scaling is more accessible, the business can grow earlier and generate more income sooner.
In addition, purely on-site storage can hinder growth, which results in high opportunity prices because the organization misses out on robust profits.
4. Control
Control is one of the main benefits of a hybrid cloud environment. So, instead of putting all facets of your IT infrastructure in the hands of third-party providers, you can personalize the private side of your cloud model to suit your organization’s requirements. Also, you can allow another sectors of your hybrid cloud to handle less critical or time-sensitive data.
5. Speed
Another benefit of managing control over your network resources is speed. While a hybrid cloud environment is not quicker than a public or multi-cloud setup, it enables the IT team to optimize the network in ways that help reduce latency and simplify the data transfer process.
Also, a hybrid environment can help you utilize the power of edge computing, making your entire IT infrastructure faster. Therefore, Public clouds are insisted to share their resources whereas the private cloud functions are personalized and designed so that the resources are utilized most effectively.
Drawbacks of Hybrid Cloud
1. Hard to Implement
From a design perspective, Initial Implementation of this cloud architecture can be more complex. Therefore, before focusing on a cloud journey, businesses must thoroughly analyze and evaluate their business requirements and work with a public cloud service supplier or provider who can easily help convert those requirements into the best hybrid cloud implementation approach.
2. Technical Complexity
As business migrate their applications and workloads to a hybrid multi-cloud environment, integration and management can become more complex. Also, as per recent estimates, today’s companies are running up to at least ten clouds, which makes them seamless integrations, robust security, and data synchronization across multiple environments facing ongoing challenges.
Also, overcoming hybrid cloud complexity requires a clear and concise strategy developed around a single cloud platform architecture that offers a fabric of cloud services.
3. Lack of visibility
In a problematic hybrid multi-cloud environment teams can face difficulty obtaining a comprehensive view of all the process, applications, and systems that come from on-premises data centers, SaaS applications, multiple clouds (private and public), and applications and data running in IoT and edge computing environments.
4. Cost Control
A hybrid multi-cloud environment requires managing different vendor services. When using multiple clouds, a typical enterprise organization also depends on numerous vendor-related SaaS applications, storage capabilities, and other services and products.
Therefore, managing multi-vendor services and controlling costs requires visibility across a single integrated platform so that IT leaders can track resource allocations and manage cloud-related prices.
How do you set up a Hybrid Cloud?
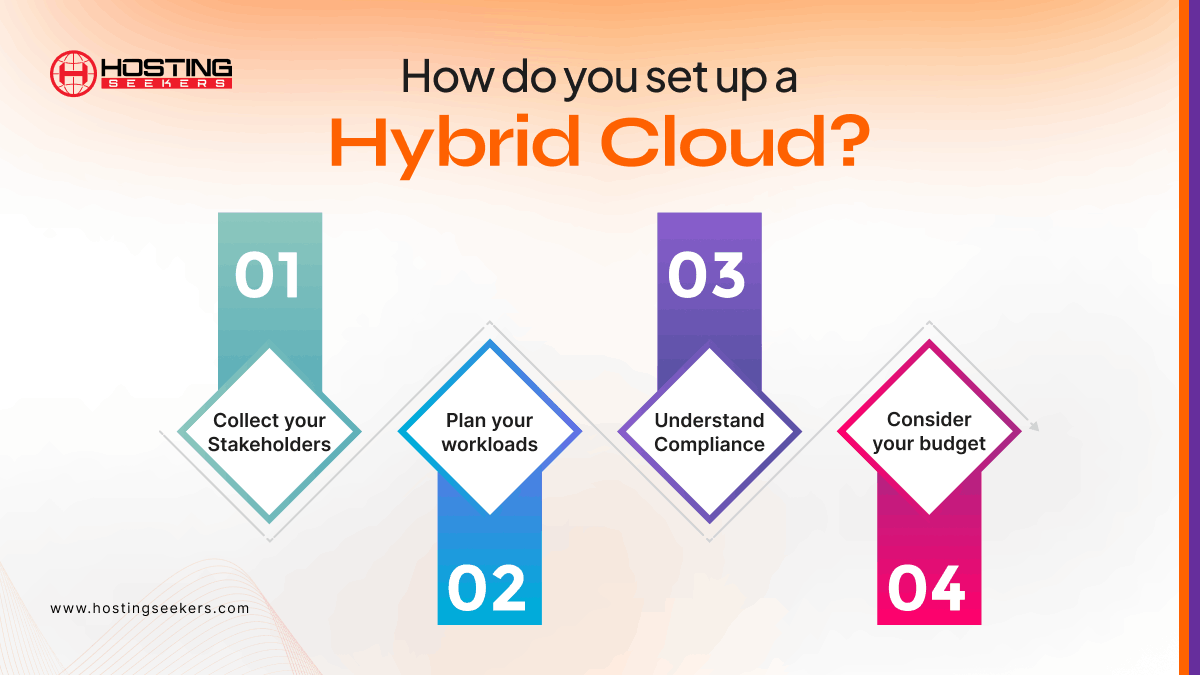

Step 1: Collect your Stakeholders
The first step in setting up hybrid cloud solutions is to plan your team. It would help if you collected input from your organization’s CTO, CIO, cloud architects, database administrators, DevOps team, and anyone with a role related to the cloud. Therefore, look for decision-makers, end users, and managers.
Based on how closely they will be working with the cloud, you can give your team members an opportunity to collaborate and be sure to provide a means of communication and collaboration.
Step 2: Plan your workloads
It is necessary to pre plan your workloads. Therefore, to maintain more control over applications, hosting these on your private cloud is best. Thus, you can more easily adjust cloud infrastructure within your private cloud to meet your needs. In addition, you can also utilize specialized tools to help scale and manage your workloads.
Step 3: Understand Compliance
Another vital step in managing your compliance is to manage your risk of breaches and follow data best practices; you can select user type, clients, or other personal data that needs to be established and followed consistently.
Make sure to leave compliance up to your vendor. Your business is ultimately responsible for your compliance. Also, you can utilize physical and database separations to protect your data. In addition, you can select a compliance champion and designate a team member to maintain your compliance program.
Step 4: Consider your budget
It would help if you considered the financial benefits of the software and hardware investments. Also, the cloud has many benefits, including organizing and managing computing resources more cost-effectively.
Consider the financial benefits that include managing computing resources more productively. So, visualize current and future usage. Also, you can plan how your cloud service can scale along with your applications.
Summing Up
Hybrid cloud solutions represent a powerful strategy for businesses looking to maximize the benefits of both private and public cloud environments. By doing so businesses can achieve greater flexibility, cost savings, and operational efficiency while maintaining high security and compliance standards.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q 1: How are hybrid clouds formed?
Ans: Hybrid clouds are formed by linking private cloud environments, such as on-premises data centers, with public cloud services like AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud. This integration typically uses networking solutions, data synchronization, and application orchestration tools to ensure seamless operation and resource sharing across the different cloud environments.
Q 2: What is a hybrid cloud, and how does it work?
Ans: It is a computing architecture that gathers private cloud (on-premises) and public cloud services, allowing data and applications to move between them. This setup enables businesses to leverage the scalability and cost-efficiency of public clouds while maintaining control and security with private clouds, ensuring optimal performance and resource allocation.
Q 3: How do you connect to a hybrid cloud?
Ans: Connecting a hybrid cloud involves using network virtualization, secure VPNs, and hybrid cloud management tools to integrate on-premises and cloud resources. APIs facilitate communication between different environments, while hybrid cloud platforms provide centralized management, monitoring, and orchestration to ensure seamless operation and secure data exchange between the connected infrastructures.
Q 4: What are the two types of hybrid clouds?
Ans: The two types of hybrid cloud are:
1) Hybrid cloud combining private clouds (on-premises or hosted) with public cloud services, enabling flexible resource usage; and
2) Multi-cloud hybrid systems, which involve integrating multiple public cloud providers to enhance redundancy, avoid vendor lock-in, and optimize performance and cost-efficiency.
Q 5: What is the main disadvantage of hybrid cloud computing?
Ans: The main disadvantage of hybrid cloud computing is the complexity of managing and securing multiple environments. This includes ensuring consistent security policies, data governance, and compliance.