Risk Assessment | Importance, Objectives, Process

What is Risk Assessment?
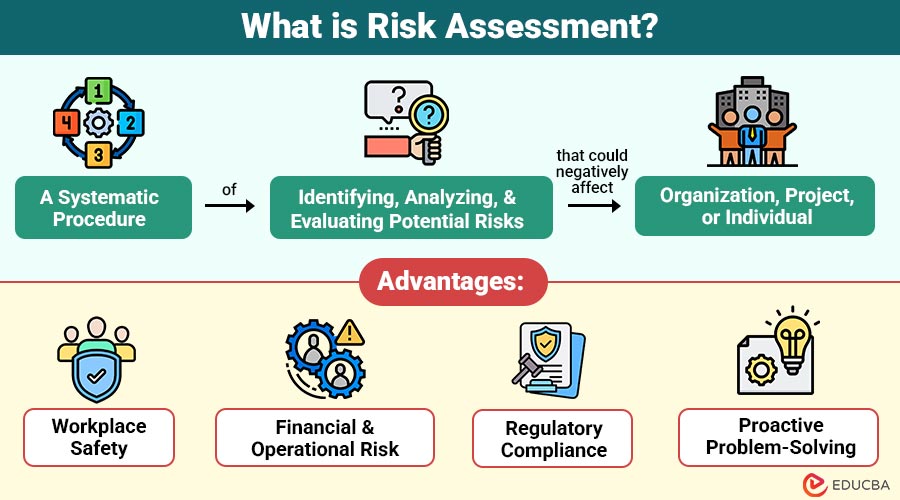
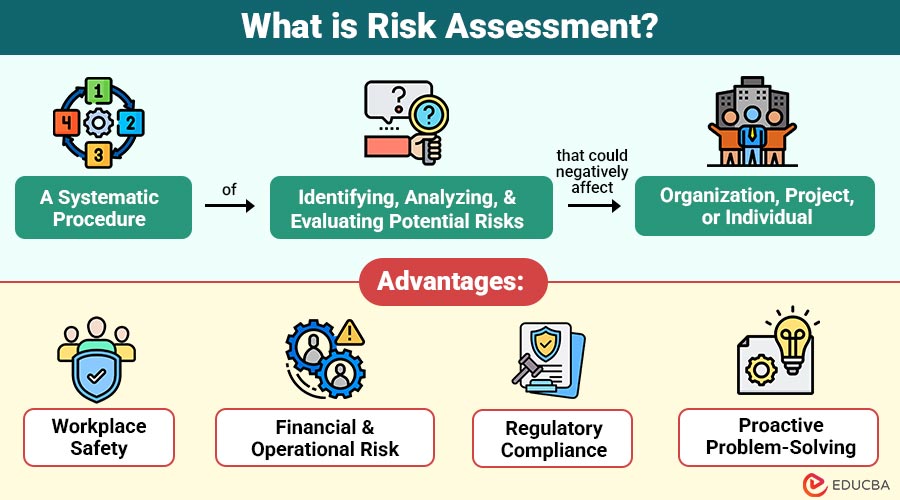
Risk Assessment is a systematic procedure of identifying, analyzing, and evaluating potential risks that could negatively affect an organization, project, or individual. The primary objective is to reduce likelihood and effect of these risks through preventive measures, contingency planning, and corrective actions.
In simple terms, it is about asking:
- What could go wrong?
- How likely is it to happen?
- What would be the impact if it did happen?
- What can we do to prevent or manage it?
Table of Contents:
Key Takeaways:
- Risk assessment enables organizations to proactively identify threats, ensuring safety, operational stability, and the protection of valuable assets.
- Evaluating potential hazards supports compliance with laws, reduces financial losses, and fosters effective stakeholder trust.
- Systematic risk analysis guides decision-making, enabling businesses to prioritize resources and respond to challenges efficiently.
- Regular assessments enhance preparedness, minimize unexpected disruptions, and improve long-term resilience across industries and projects.
Importance of Risk Assessment
Risk assessment is essential across various industries, including healthcare, construction, IT, finance, and manufacturing. Its importance can be understood in several dimensions:
1. Protects People and Assets
Risk assessment identifies hazards, ensuring employee safety, preventing accidents, and protecting physical and digital assets from potential harm.
2. Compliance with Regulations
It helps organizations meet industry-specific laws, safety standards, and cybersecurity requirements, avoiding fines, legal issues, and reputational damage.
3. Business Continuity
By anticipating disruptions such as natural disasters or cyberattacks, organizations can develop plans that enable them to maintain operations without significant downtime.
4. Financial Stability
Conducting risk assessments helps organizations reduce unexpected losses, avoid financial penalties, and protect investments, ensuring efficient use of resources.
5. Reputation Management
Proactively managing risks demonstrates responsibility, builds stakeholder trust, and enhances public perception, strengthening brand credibility and market confidence.
6. Strategic Planning
It provides data-driven insights that guide leadership decisions, enabling the effective allocation of resources and prioritization of high-impact organizational objectives.
Objectives of Risk Assessment
The primary objectives of risk assessment include:
1. Protecting People
Risk assessment identifies workplace hazards, implements safety measures, and reduces health risks, thereby ensuring employee well-being and minimizing the likelihood of injuries.
2. Protecting Assets
It evaluates threats to property, equipment, and infrastructure, applying preventive measures to reduce damage and maintain organizational resources.
3. Compliance
Ensures adherence to legal, regulatory, and industry standards, avoiding fines, legal penalties, and reputational damage from non-compliance.
4. Operational Continuity
Assesses risks that could disrupt core operations, enabling organizations to implement contingency plans and maintain seamless business processes.
5. Financial Protection
Identifies potential financial risks, such as fraud, accidents, or crises, and implements controls to prevent losses and safeguard organizational resources.
6. Reputation Management
Proactively managing risks protects the organization’s image, builds stakeholder confidence, and maintains trust with clients, partners, and the public.
Types of Risk Assessment
Risk assessments vary depending on the industry, context, and goals. The main types include:
1. Qualitative Risk Assessment
Relies on expert judgment and descriptive methods to evaluate risks, categorizing them as low, medium, or high, often using checklists for workplace hazards.
2. Quantitative Risk Assessment
Utilizes numerical data, probability models, and statistics to assess the likelihood and financial implications of risks, offering precise and measurable insights for informed decision-making.
3. Generic Risk Assessment
Broad assessment of common risks across an industry or activity, addressing general hazards like equipment use, falls, or standard operational procedures.
4. Site-Specific Risk Assessment
Customized evaluation for a particular location or project, identifying risks unique to that environment, such as chemical exposure, machinery hazards, or local operational challenges.
5. Dynamic Risk Assessment
Conducted in real-time, adapting to evolving conditions, especially in emergencies, allowing rapid decisions to mitigate risks during situations like fire rescues or natural disasters.
Risk Assessment Process
Risk assessment typically follows a structured step-by-step process:
1. Identify Hazards
Collect information on potential physical, financial, technological, or environmental risks using inspections, historical data, and expert insights.
2. Determine Who or What May Be Affected
Organizations should identify employees, customers, assets, processes, or communities that each hazard could potentially impact to understand their exposure and vulnerability.
3. Analyze Risks
Utilize scoring systems, probability matrices, and statistical or financial modeling to assess each risk’s likelihood and possible outcomes.
4. Evaluate and Prioritize Risks
Rank risks based on severity and probability, focusing resources on high-priority risks with the greatest potential impact.
5. Implement Control Measures
Apply risk management strategies such as avoidance, mitigation, transfer, or acceptance; for example, installing fire suppression systems to mitigate risks.
6. Document and Communicate
Maintain detailed reports of identified risks, analyses, and controls, and share findings with stakeholders, employees, and management.
7. Review and Update
Regularly revisit risk assessments to account for new threats, operational changes, and evolving organizational or environmental conditions.
Advantages of Risk Assessment
Here are some key advantages of conducting a risk assessment:
1. Workplace Safety
It identifies hazards, implements preventive measures, and reduces accidents or injuries, creating a safer working environment for employees and visitors.
2. Financial & Operational Risk
By anticipating potential losses and operational disruptions, organizations can implement controls to protect assets, reduce costs, and ensure smooth business operations.
3. Regulatory Compliance
Helps organizations adhere to industry, safety, environmental, and cybersecurity standards, avoiding penalties, fines, and legal consequences.
4. Proactive Problem-Solving
Organizations identify potential challenges early, allowing timely mitigation, contingency planning, and decision-making before risks escalate into serious issues.
Disadvantages of Risk Assessment
Here are some disadvantages associated with risk assessments:
1. Time & Cost
Comprehensive risk assessments require significant time, resources, and financial investment, which may strain smaller organizations or projects.
2. Expertise & Data
Effective assessments rely on skilled personnel and reliable data; inaccuracies or lack of knowledge can lead to flawed results.
3. Residual Risk
Even when organizations conduct thorough assessments, unforeseen events or new threats can arise, so they can only reduce risk, not eliminate it completely.
4. Model Limitations
Relying heavily on quantitative models may cause organizations to overlook unpredictable, rare, or context-specific risks that existing frameworks do not capture.
Real World Examples
Here are some practical examples of risk assessment across various industries:
1. Healthcare
Hospitals and healthcare facilities perform risk assessments to prevent infections, manage medical equipment failures, ensure patient safety, and comply with healthcare regulations and safety standards.
2. Information Technology
IT companies assess cybersecurity risks, including phishing, malware, data breaches, and system downtime, and implement preventive measures, backups, and employee training to protect sensitive information.
3. Construction Industry
Construction firms identify hazards such as falls, machinery accidents, chemical exposure, and structural failures, applying safety protocols, protective equipment, and monitoring systems to safeguard workers.
4. Financial Institutions
To protect consumer money, comply with legal requirements, and reduce possible losses, banks and other financial institutions evaluate credit, investment, operational, and regulatory risks.
5. Environmental Sector
Government agencies and environmental organizations conduct risk assessments to manage pollution, natural disasters, and the impacts of climate change, implementing mitigation strategies to ensure public and ecological safety.
Final Thoughts
Risk assessment is a vital framework that helps organizations manage uncertainty effectively. By identifying hazards, analyzing their impacts, and implementing controls, businesses can protect their employees, assets, finances, and reputation. Although risks can not be fully eliminated, proactive assessments support informed decisions, enhance resilience, and ensure long-term sustainability, making them essential for leaders, compliance officers, and project managers alike.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. What are the key tools used in risk assessment?
Answer: Tools include risk matrices, fault tree analysis, SWOT analysis, HAZOP studies, and checklists.
Q2. How often should risk assessments be conducted?
Answer: At least annually or whenever significant changes occur in operations, processes, or regulations.
Q3. Who is responsible for conducting risk assessments?
Answer: Employers, safety officers, compliance teams, or specialized risk management consultants.
Q4. Is risk assessment only for large companies?
Answer: No, small and medium-sized businesses also benefit greatly, especially in areas such as workplace safety and financial planning.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Risk Assessment” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.
- Risk Assessment Example
- Relative Risk Reduction Formula
- Risk Management in Trading
- Reducing Risk in Product Development